Suksai Aarif さんが 23rd International Conference of Asia Digital Art and Design Association にて Best Paper Presentations を受賞
- 電気電子情報工学専攻
受賞者
Suksai Aarifさん(電気電子情報工学専攻専攻1年)
指導教員
Peeraya Sripian 准教授(工学部 先進国際課程/Innovative Global Program)
学会・大会名
賞名
Toward Improving Audibility of Multiple Simultaneous Voices in Virtual Poster Presentation
仮想ポスター発表における複数同時音声の可聴性向上に向けて

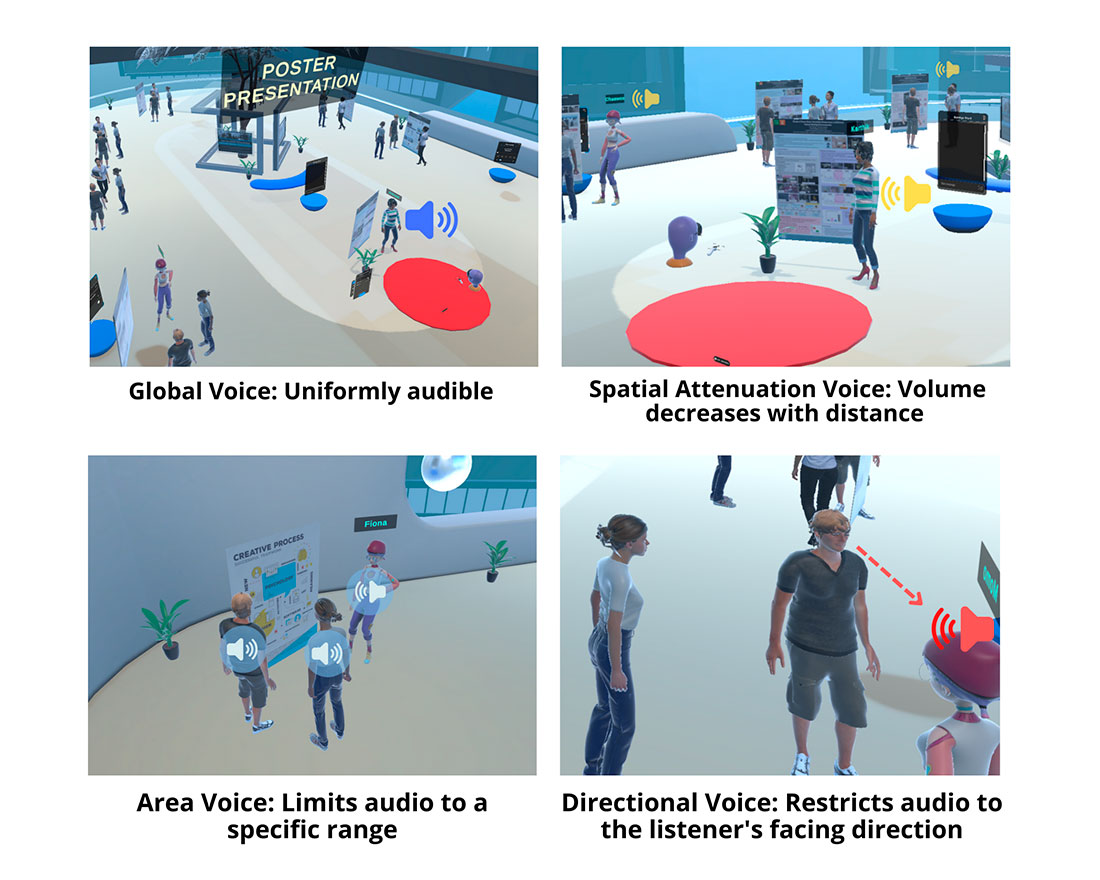
This study investigates how various audio models in Virtual Reality (VR) influence communication efficiency, clarity, and user comfort during social interactions. While VR systems support social collaboration, current audio design often relies on simple spatialization, failing to mimic how humans naturally perceive sound direction, distance, and focus. To address this, the study compares four models—non-spatial, spatial, area-based, and directional audio—to evaluate their impact on user interaction and presence. Participants perform collaborative tasks in VR while researchers collect subjective data (questionnaires on immersion and comfort) and objective data (heart rate variability to assess cognitive load). The goal is to identify audio configurations that maximize clarity while minimizing auditory fatigue.
本研究は、バーチャルリアリティ(VR)空間における多様な音響モデルが、社会的なインタラクション中のコミュニケーション効率、音声の明瞭性、およびユーザーの快適性に与える影響を調査するものです。VRにおける社会的な協調作業は増加していますが、現在の音響設計は単純な空間化に留まることが多く、人間が現実世界で音の方向、距離、焦点をどのように認識しているかという点は十分に考慮されていません。 本研究では、非空間音響、空間音響、エリアベース音響、および指向性音響の各モデルを比較し、ユーザーの相互作用や臨場感への影響を評価します。参加者は異なる音響条件下でVR内の協調タスクを行い、快適性や没入感に関するアンケート(主観的指標)と、認知負荷やストレスを測定するための心拍変動(客観的指標)の両面からデータを収集します。本研究の目的は、聴覚疲労や不快感を抑えつつ、明瞭性を向上させる最適な音響モデルを特定することにあります。
The primary goal is to identify VR audio models that maximize communication efficiency and user comfort. By analyzing how different sound environments influence human perception, the study aims to bridge the gap between conventional audio systems and the complex requirements of high-stakes virtual collaboration.
VR環境において、コミュニケーションの明瞭性とユーザーの快適性を両立させる音響モデルを確立することを目的としています。高度な音響設計が人間の知覚や協調行動に与える影響を明らかにすることで、従来のシステムを超えた、より自然な仮想コミュニケーション環境の構築を目指します。
今後の展望
These findings provide a foundation for the design of human-centered VR systems in education, remote collaboration, and healthcare. Optimizing audio presentation can significantly reduce mental fatigue and improve the efficacy of virtual teamwork. Key remaining challenges include individual differences in auditory perception and the integration of adaptive systems that dynamically respond to a user’s physiological state.
本研究の知覚データは、教育、遠隔コラボレーション、医療トレーニングといった分野における人間中心のVRシステム設計の基盤となります。音響提示を最適化することで、長時間の作業による精神的疲労を軽減し、共同作業の質を向上させることが可能です。今後は、個々人の知覚特性への対応や、ユーザーの生理状態に動的に反応する適応型システムの構築が重要な課題となります。