Multiple Health Benefits of B-type Procyanidin-rich Foods like Chocolate and Apples Consumed in Right Amounts
2022/10/05
- Research
Researchers shed light on how an optimal intake of electrophilic compounds like procyanidins is linked to hormesis of hemodynamic and metabolic responses
Procyanidins are a class of polyphenols (plant metabolites) that are abundantly found in nature. The B-type procyanidins are one of the most commonly consumed catechin oligomers in the human diet. Previous studies have shown both the long-term and single-dose advantages of B-type procyanidins on human metabolism, circulation, and the nervous system. Now researchers review the hormetic effects of B-type procyanidins exerted on the primary target organ, the gut, via activation of the central nervous system.
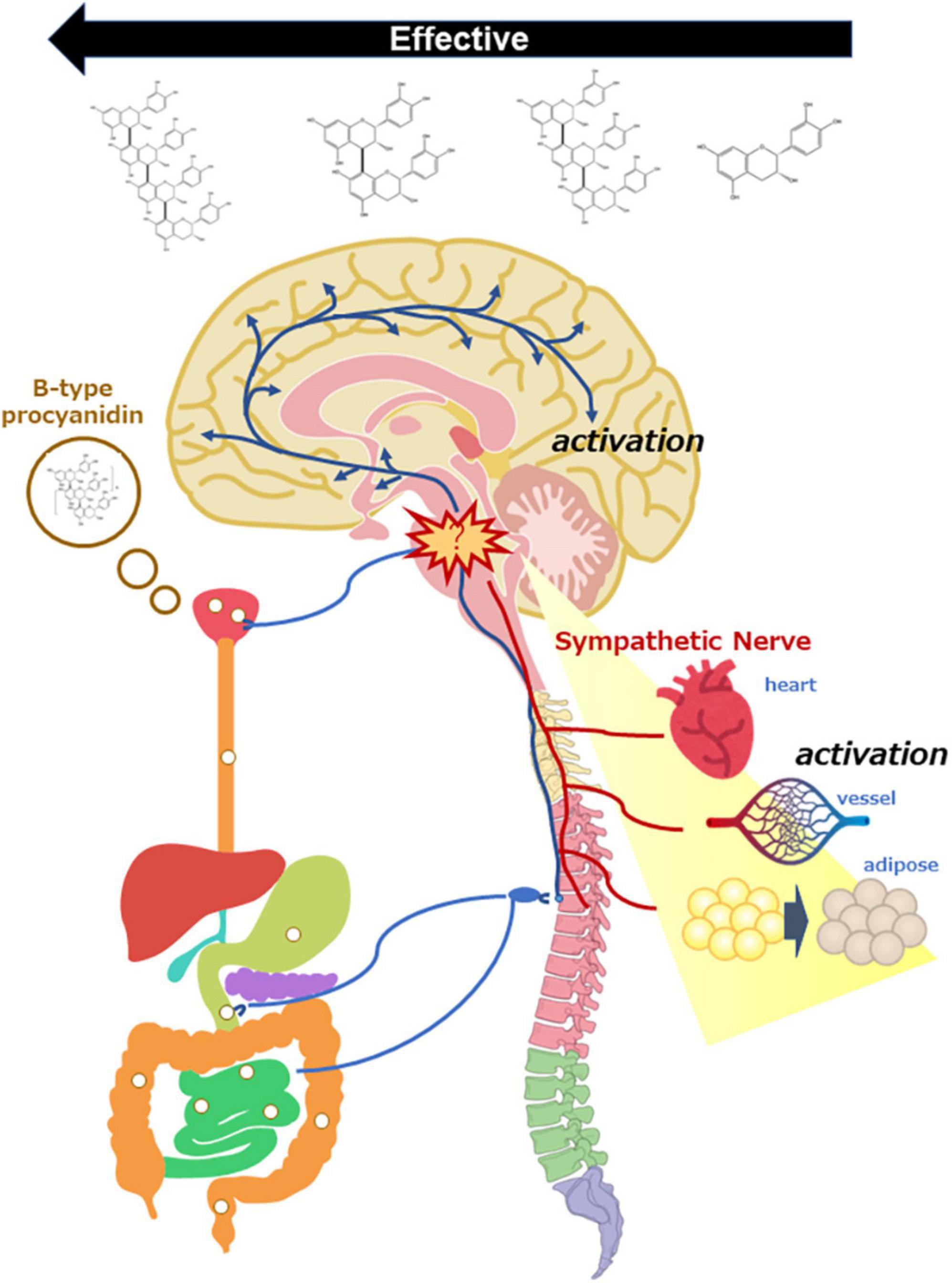
Title:Hormetic response is induced in mammals in response to stressors including B-type procyanidins and involves neuromodulation via the gut-brain axis
Caption:Researchers from SIT, Japan investigated the dose-response effects of B-type procyanidins on the hormetic response system
Credit:Reprinted with permission from, Osakabe N, Fushimi T and Fujii Y (2022) Hormetic response to B-type procyanidin ingestion involves stress-related neuromodulation via the gut-brain axis: Preclinical and clinical observations. Front. Nutr. 9:969823. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.969823.Copyright © 2022 Osakabe, Fushimi and Fujii.
License Type:CC BY 4.0
Usage restrictions:Use under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). You are free to share and adapt the material. Attribution is required, with a link to the license, and you must indicate if changes are made to the work. Further details are available athttps://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Image link:https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.969823/full
The dose-response relationship of most bioactive compounds follows a monotonic pattern, in which a higher dose shows a greater response. However, in some exceptional cases, a U-shaped dose-response curve is seen. This U-shaped curve signifies hormesis—an adaptive response, in which a low dose of usually a harmful compound induces resistance in the body to its higher doses. This means that exposure to low levels of a harmful trigger can induce the activation of stress-resistant pathways, leading to greater repair and regeneration capabilities. In case of B-type procyanidins, several in vitro studies support their hormetic effects, but these results have not been demonstrated in vivo.
To address this knowledge gap, researchers from Shibaura Institute of Technology (SIT), Japan, led by Professor Naomi Osakabe from the Department of Bioscience and Engineering, reviewed the data from intervention trials supporting hormetic responses of B-type procyanidin ingestion. The team, comprising Taiki Fushimi and Yasuyuki Fujii from the Graduate School of Engineering and Science (SIT), also conducted in vivo experiments to understand possible connections between B-type procyanidin hormetic responses and CNS neurotransmitter receptor activation. Their article was made available online on June 15, 2022 and has been published in volume 9 of Frontiers of Nutrition on September 7, 2022.
The researchers noted that a single oral administration of an optimal dose of cocoa flavanol temporarily increased the blood pressure and heart rate in rats. But the hemodynamics did not change when the dose was increased or decreased. Administration of B-type procyanidin monomer and various oligomers produced similar results. According to Professor Osakabe, “These results are consistent with those of intervention studies following a single intake of food rich in B-type procyanidin, and support the U-shaped dose-response theory, or hormesis, of polyphenols.”
To observe whether the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is involved in the hemodynamic changes induced by B-type procyanidins, the team administered adrenaline blockers in test rats. This successfully decreased the temporary increase in heart rate induced by the optimal dose of cocoa flavanol. A different kind of blocker—a1 blocker—inhibited the transient rise in blood pressure. This suggested that the SNS, which controls the action of adrenaline blockers, is responsible for the hemodynamic and metabolic changes induced by a single oral dose of B-type procyanidin.
The researchers next ascertained why optimal doses, and not high doses, are responsible for the thermogenic and metabolic responses. They co-administered a high dose of cocoa flavanol and yohimbine (an α2 blocker) and noted a temporary but distinct increase in blood pressure in test animals. Similar observations were made with the use of B-type procyanidin oligomer and yohimbine. Professor Osakabe surmises, “Since α2 blockers are associated with the down-regulation of the SNS, the reduced metabolic and thermogenic outputs at a high dose of B-type procyanidins seen in our study may have induced α2 auto-receptor activation. Thus, SNS deactivation may be induced by a high dose of B-type procyanidins.”
Previous studies have proven the role of the gut-brain axis in controlling hormetic stress-related responses. The activation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis by optimal stress has a strong influence on memory, cognition, and stress tolerance. This article highlights how HPA activation occurs after a single dose of B-type procyanidin, suggesting that stimulation with an oral dose of B-type procyanidin might be a stressor for mammals and cause SNS activation.
Hormesis and its triggering biochemical pathways deliver protection against various pathological and aging processes, enhancing our general health and making us resilient to future stress. Though the exact relation between B-type procyanidins and the CNS needs more research, the health benefits of B-type procyanidin-rich foods remains undisputed.
Reference
| Title of original paper: | Hormetic response to B-type procyanidin ingestion involves stress-related neuromodulation via the gut-brain axis: Preclinical and clinical observations |
| Journal | Frontiers in Nutrition |
| DOI: | 10.3389/fnut.2022.969823 |
Funding Information
This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number: 19H04036).Contact
Planning and Public Relations Section
3-7-5 Toyosu, Koto-ku, Tokyo 135-8548, Japan (2F the Centennial Main Building, Toyosu Campus)
TEL:+81-(0)3-5859-7070 / FAX:+81-(0)35859-7071
E-mail:koho@ow.shibaura-it.ac.jp